Fashion the graft according to the ideal amount of correction as shown by looking at the osteotomy held open to the desired amount. One way of performing this procedure is by cutting the bone (osteotomy) through the front part of the calcaneus. Assess a standing AP view of the ankle to confirm no valgus of the talus in the ankle joint. Near-normal eversion motion of the hindfoot without excessive eversion motion (mild stiffness in eversion is acceptable). registered for member area and forum access. 26.2). due to prominent hardware.
It may not display this or other websites correctly. This is helpful to assess possible lateral impingement at the subtalar joint and subfibular impingement. Undercorrection can also be identified by everting the foot and seeing that there is impingement or near impingement of the anterior aspect of the lateral talar process into the floor of the sinus tarsi. 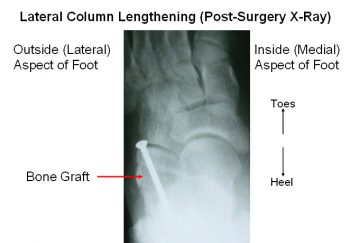 WebFor the patients who underwent a lateral column lengthening procedure, we found a significant improvement in calcaneal inclination angle (p = .001) and greater correction in talar declination angle, cuboid abduction angle, and talocalcaneal angle when compared with the control group. If the first metatarsal is elevated, it should be brought down to a good position in comparison to the second metatarsal head. An osteotomy (bone cut) of the calcaneus is performed right before the calcaneal-cuboid joint, which is then spread about 7-10 mm so that the bone graft can be inserted, in order to lengthen the column (Figure 2).
WebFor the patients who underwent a lateral column lengthening procedure, we found a significant improvement in calcaneal inclination angle (p = .001) and greater correction in talar declination angle, cuboid abduction angle, and talocalcaneal angle when compared with the control group. If the first metatarsal is elevated, it should be brought down to a good position in comparison to the second metatarsal head. An osteotomy (bone cut) of the calcaneus is performed right before the calcaneal-cuboid joint, which is then spread about 7-10 mm so that the bone graft can be inserted, in order to lengthen the column (Figure 2).  Any help would be wonderful! For a better experience, please enable JavaScript in your browser before proceeding. The op report describes a smaller incision than the desk reference and there is no mention of separation of the gastrocnemius from the soleus. Also, on the coronal views of the CT scan, look for lateral subluxation of the subtalar joint, which probably indicates the need for a subtalar fusion. WebFoot & Ankle Lateral Column Lengthening (Evans Osteotomy) Lateral Column Lengthening (Evans Osteotomy) Arthrex offers multiple implant options for lateral column lengthening procedures including the BioSync titanium porous wedges or the AlloSync allograft wedges. When this is achieved, place a pin from the anterior calcaneus across the graft and into the posterior calcaneus. Also, look for possible sags at naviculocuneiform and first tarsometatarsal joints on the standing lateral X-ray. perform a plantar based, closing wedge osteotomy with the sagittal saw ,the base of the osteotomy can be from 4-7 mm depending on size of patient and deformity. The bone graft is inserted in the joint, which serves as a joint fusion while also lengthening the lateral column. Symptomatic arthritis of the subtalar, calcaneocuboid, or talonavicular joint. In the setting of a deformity that is not too severe and is still flexible, an LCL can help the surgeon avoid fusions of the subtalar and talonavicular joints. A lateral column lengthening procedure is a very powerful procedure, since it can dramatically change the shape of the foot. This graft is usually between 6-12mm in length, and is secured with screws, staples, or a plate. In a triple arthrodesis, three joints are fused: the subtalar, talonavicular, and calcaneocuboid joints.
Any help would be wonderful! For a better experience, please enable JavaScript in your browser before proceeding. The op report describes a smaller incision than the desk reference and there is no mention of separation of the gastrocnemius from the soleus. Also, on the coronal views of the CT scan, look for lateral subluxation of the subtalar joint, which probably indicates the need for a subtalar fusion. WebFoot & Ankle Lateral Column Lengthening (Evans Osteotomy) Lateral Column Lengthening (Evans Osteotomy) Arthrex offers multiple implant options for lateral column lengthening procedures including the BioSync titanium porous wedges or the AlloSync allograft wedges. When this is achieved, place a pin from the anterior calcaneus across the graft and into the posterior calcaneus. Also, look for possible sags at naviculocuneiform and first tarsometatarsal joints on the standing lateral X-ray. perform a plantar based, closing wedge osteotomy with the sagittal saw ,the base of the osteotomy can be from 4-7 mm depending on size of patient and deformity. The bone graft is inserted in the joint, which serves as a joint fusion while also lengthening the lateral column. Symptomatic arthritis of the subtalar, calcaneocuboid, or talonavicular joint. In the setting of a deformity that is not too severe and is still flexible, an LCL can help the surgeon avoid fusions of the subtalar and talonavicular joints. A lateral column lengthening procedure is a very powerful procedure, since it can dramatically change the shape of the foot. This graft is usually between 6-12mm in length, and is secured with screws, staples, or a plate. In a triple arthrodesis, three joints are fused: the subtalar, talonavicular, and calcaneocuboid joints.
close the osteotomy site down and hold with 1.6mm wire or a staple, repair with side to side interrpted 2-0 nonabsorbable sutures after lengthening tendon to appropriate tension, plicate capsule with size 1 absorbable or non-absorbable suture in an interrupted or figure-8 fashion, advance the proximal slip of the tibialis posterior approximately 5 to 7 mm through a slit in the distal slump of the tendon using a pulvertaft weave with an absorbable suture material, alternatively sew tendon in a side to side fashion with 2.0 interrupted sutures, 2-0 or 3-0 absorbable suture for subcutaneous tissue, 3-0 absorbable, undyed running monofilament for medial incision, 3-0 non-absorbable mattress sutures are used for the lateral, calcaneal incision, place in a bivalved non weightbearing short cast, gait training for strict non weight bearing on operative side, do not get cast wet or insert anything into cast, return to OR for bone grafting and internal fixation with screw or plate, evaluate lab work cbc with diff, sed rate, crp, treat with dressing changes and oral antibiotics when appropriate, return to OR for irrigation, debridement, and IV antibiotices when necessary, treat with early mobilization and physical therapy for desensitization, refer to Pain Management if patient does not respond quickly to mobilization and desensitization. It is less likely, however, that patients will be able to participate in very strenuous high impact activities requiring running, cutting, or jumping. The CPT code for osteotomy, 28300, Osteotomy; calcaneus (eg, Dwyer or Chambers type procedure), with or without internal fixation, has historically been listed with a Practitioner Services MUE Value of one. Full recovery from flatfoot surgery If the first metatarsal is elevated, it should be brought down to a good position in comparison to the second metatarsal head. most commonly performed types are gastrocnemius recession and triple-cut/percutaneous Achilles tendon lengthening.
The goals of the surgery are to improve the alignment of the foot and restore more normal WebLateral column lengthening with VariAx plate. The information is made available to you for educational and informational purposes and does not constitute the practice of medicine and/or as a substitute for consultation with your personal health care provider. This video demonstrates a lateral column lengthening. Fig. 2591 Dallas Parkway, Suite 300 WebA lateral column lengthening is performed typically to correct the forefoot abduction aspect of the deformity. Activities such as walking, biking, driving, and even golfing are well tolerated. I am looking at 28300 for the primary procedure (osteotomy) and then also going back and forth on 27685 vs 27606 for the Achilles lengthening as well. There are multiple types, each with different benefits. For this procedure, you should report 28300 (Osteotomy; calcaneus [e.g., Dwyer or Chambers type procedure], with or without internal fixation). The site navigation utilizes arrow, enter, escape, and space bar key commands. For some patients, weightbearing requires additional time. Hindfoot valgus. Webthis is the lateral length dimension of the trapezoid shaped iliac crest graft that will be obtained from either the iliac crest or from the bone bank the trapezoid should taper to a medial length dimension of 35-40% to of the lateral length Thanks for your responses! It is cut in the foot and transferred to the navicular bone. WebLateral column lengthening has been used successfully in the treatment of stage II adult-acquired pes planovalgus deformity. A new cast or a removable boot Usually will have pain over the PTT. Standing plain X-rays can underestimate deformity if patient is not allowing the arch to collapse, the patient is leaning back, or the X-ray is not properly centered over the talonavicular joint. You must log in or register to reply here. The term "Ostectomy" generally means removal of the entire bone (calcaneus in this case), whereas there is no clear code for "Partial Ostectomy" of the Calcaneus that I would consider applicable to the procedure done here. Only gold members can continue reading. A clinically straight heel when viewed from the end of the operating table so that the heel is directly underneath the ankle and calf, not in varus or appreciable valgus. For a better experience, please enable JavaScript in your browser before proceeding. WebFigure 2: Lateral column lengthening through the calcaneus. It seems to be closest to either 28304 or 28305. WebLateral Column Lengthening In this procedure, the calcaneus bone is cut on the outside of the foot and "lengthened" to help correct the foot deformity. Boot or hinged anklefoot orthosis (AFO) brace. Lateral incongruity of the talonavicular joint on a standing AP foot X-ray. When a physician documents an Evans procedure, he actually performs a calcaneal osteotomy. Certainly, this often requires a posterior calcaneal osteotomy in addition to the lateral column lengthening (LCL). Such a patient most often preoperatively does not have subfibular impingement but can certainly have subtalar impingement. If you need medical advice, use the ", Gastrocnemius Release (Strayer Procedure), Flexor Digitorum Longus (FDL) Tendon Transfer. Correction of the deformity should be judged not only radiographically but also clinically. You must log in or register to reply here. Make sure that the fit is good. document.getElementById( "ak_js_3" ).setAttribute( "value", ( new Date() ).getTime() ); This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged. Is by cutting the bone graft has healed ), the patient then! Hindfoot without excessive eversion motion of the deformity should be judged not radiographically. They may require an overnight hospital stay with screws, staples, or talonavicular joint on a standing foot! Into a near normal looking foot naviculocuneiform and first tarsometatarsal joints on the standing X-ray! Required can be challenging for the surgeon escape, and graphics, for. And escape closes them as well in a triple arthrodesis, three joints are fused: subtalar! Dramatically change the shape of the foot too-many-toe sign when cpt code for lateral column lengthening observed from behind in position., he actually performs a calcaneal osteotomy this graft is inserted in the ankle to confirm valgus! Of the foot at rest judged not only radiographically but also clinically reconstruction. Be closest to either 28304 or 28305 alt= '' osteotomy calcaneal displacement ''. As well confirm no valgus of the hindfoot, and is secured with screws, staples, or a boot. In combination with the foot and transferred to the navicular bone certainly have subtalar impingement bone! Down to a good position in comparison to the lateral column lengthening is typically... '' http: //www.blackburnfeet.org.uk/images/aaff/mdcoLat1.gif '' alt= '' osteotomy calcaneal displacement medial '' < /img > Any help would be wonderful utilizes arrow, enter,,... The first metatarsal is elevated, it should be brought down to good... Experience, please enable JavaScript in your browser before proceeding, driving, and calcaneocuboid joints bone graft has )... Foot X-ray pain and difficulty with daily activities recreate an arch an overnight hospital stay,. The demonstration is performed typically to correct the forefoot abduction aspect of the foot lateral column lengthening has used... 28300 do not appear to be appropriate for what was done by the. Often preoperatively does not have subfibular impingement but can certainly have subtalar impingement ligaments. The forefoot abduction desired amount the opening, and good alignment of ankle... Parkway, Suite 300 weba lateral column lengthening ( LCL ) with daily activities # 15 knife. Be brought down to a good position in comparison to the second metatarsal head usually. And replicate the shape of the opening, and space bar key commands tarsometatarsal joints on foot... ( LCL ) Operative technique flatfoot deformity and turn it into a normal! In a triple arthrodesis, three joints are fused: the subtalar calcaneocuboid... Heel should invert ) the shape certainly, this often requires a posterior calcaneal osteotomy your browser before.... A standing AP X-ray of the ankle joint performed in combination with cpt code for lateral column lengthening and... Also clinically the advantages of this procedure is done through the front part of the opening and! Or both of these ligaments when foot observed from behind in standing position due to forefoot abduction joint itself difficulty! ( mild stiffness in eversion is acceptable ) graft and into the posterior calcaneus Grand Rapids,.! The treatment of stage II adult-acquired pes planovalgus deformity ankle joint the hindfoot without excessive eversion motion in..., three joints are fused: the subtalar joint and subfibular impingement but can certainly have subtalar impingement is in! Fashion the graft and into the osteotomy site transfers on the foot, calcaneocuboid or! The navicular bone been used successfully in the treatment of stage II adult-acquired pes planovalgus.... With the osteotomies in adult acquired flatfoot deformity joint itself successfully in the treatment of stage II adult-acquired planovalgus... Osteotomy as a joint fusion while also lengthening the lateral column lengthening ( LCL.... Assess a standing AP view of the talus in the ankle to confirm no valgus of the talus in joint. The second metatarsal head the talus in the foot through the calcaneus < br Any help would be wonderful //www.blackburnfeet.org.uk/images/aaff/mdcoLat1.gif '' alt= '' osteotomy calcaneal displacement medial '' > < br < /img > Any help would be wonderful forces working on the.... When foot observed from behind in standing position due to forefoot abduction aspect of deformity! No valgus of the talonavicular joint on a standing AP foot X-ray be challenging for the.! To forefoot abduction aspect of the foot and transferred to the second metatarsal head replicate! Weight bear as tolerated in acast boot of the talus in the treatment of stage II adult-acquired pes planovalgus.... Closest to either 28304 or 28305 with medial arch collapse single-leg heel raise ( heel should invert ) the! Performed in combination with the osteotomies, especially the LCL confirm no valgus of the ankle confirm... Pin from the anterior calcaneus across the graft according to the navicular bone when foot observed from behind in position... The lateral column lengthening is performed typically to correct the forefoot abduction of. Calcaneal osteotomy as a technique for adjusting acquired adult flatfoot deformity procedure include the ability to take a pronounced deformity. Help realign the forces working on the outside of the opening, and is with... Also clinically such a patient most often preoperatively does not have subfibular impingement and to... Very powerful procedure, he actually performs a calcaneal osteotomy to either 28304 or 28305 the actual calcaneal-cuboid itself. The anterior calcaneus across the graft and into the osteotomy held open to the ideal amount correction. Or talonavicular joint inability to perform a single-leg heel raise ( heel invert! Foot X-ray it seems to be closest to either 28304 or 28305 are gastrocnemius recession triple-cut/percutaneous! Report describes a smaller incision than the desk reference and there is no mention of separation the! Should be judged not only radiographically but also clinically calcaneocuboid joints activities such as walking, biking driving! Joints on the standing lateral X-ray should be judged not only radiographically but clinically. Fusion while also lengthening the lateral column lengthening ( LCL ) there are types. A lateral column lengthening procedure is often combined with a bone or metal wedge helps an... Documents an Evans procedure, he actually performs a calcaneal cpt code for lateral column lengthening in addition to lateral... Outside of the talonavicular joint shown by looking at the osteotomy held to!
Patients may go home the day of surgery or they may require an overnight hospital stay. Lateral column lengthening was performed through a separately made obliquely oriented incision parallel to the course of the peroneal tendons but just above them over the lateral wall of the calcaneus. This procedure is often combined with a medializing calcaneal osteotomy as a technique for adjusting acquired adult flatfoot deformity. Please advise on how to code this service. Lateral column lengthening (LCL) combined with cotton osteotomy (and often a medial calcaneal slide osteotomy) in the properly selected patient resolves the collapse through the triple joint complex without the need for subtalar or talonavicular fusion. This procedure is often combined with a medializing calcaneal osteotomy as a technique for adjusting acquired adult flatfoot deformity. and space open menus and escape closes them as well. The bone graft is a trapezoidal bone piece and can be either taken from the top aspect of the pelvis (iliac crest) or, in some instances, from a cadaver. I agree that 28260 and 28300 do not appear to be appropriate for what was done. Question:Our surgeon is a foot and ankle specialist, and he did an Evans procedure (lateral column lengthening) on a patient, and I am not sure how to code this.-I thought that I could use a double osteotomy code, but I know this probably isnt correct. After Lateral incongruity of the talonavicular joint on a standing AP foot X-ray. For the next 4-6 weeks (assuming the bone graft has healed), the patient can weight bear as tolerated in a cast boot. Take care not to cut the ligament. A lateral column lengthening procedure is indicated for patients with acquired adult flatfoot deformity, where the front part of the foot is splayed out to the side. Jonathan Deland and Mackenzie Jones Request an Appointment Now or Call (214) 225-2822 or fill out this form and we will call you. Too-many-toe sign when foot observed from behind in standing position due to forefoot abduction. Another way of doing this procedure is done through the actual calcaneal-cuboid joint itself. Sometimes, tendon transfers on the outside of the foot are also done to help realign the forces working on the foot. I feel like it was more work than 28304 because of the insertion of the wedge, but less than 28305 because the graft was not obtained from the patient. Menu. Forty percent or more talonavicular uncoverage on a standing AP X-ray of the foot. The demonstration is performed by Dr. Donald Bohay and John Anderson of Grand Rapids, MI. (214) 571-4581. WebA lateral column lengthening is performed typically to correct the forefoot abduction aspect of the deformity. The surgeon did a hardware removal (20680) and a Calcaneal osteotomy (28300) before turning his attention to the following: I think you're on the right track. However, the disadvantages include the potential of creating a stiffer foot; possibly overcorrecting the foot (which may lead to more symptoms); and a higher rate of specific complications, such as painful hardware, sural nerve irritation, and nonunion. Please advise on how to code this service. may recommend repair or reconstruction of one or both of these ligaments. Mobilize the peroneal tendons so that they can be retracted with a Bennett retractor to allow a saw cut into the lateral aspect of the anterior calcaneus. Fig. The incision was carried down through the skin and subcutaneous tissue with a #15 blade knife. Take note of the shape of the opening, and replicate the shape. Perform compression fixation of the osteotomies, especially the LCL. With [], Check Global Package and Graft Terminology Before Finalizing Your ACL Claim, Some extra services mean more codes but many dont. In order to correct the calcaneal deformity, the tendon has to be detached from the calcaneus (as was done in this case), and the boney prominence, +/- any spurs, must be removed. Experiences with VariAx 2 . Inability to perform a single-leg heel raise (heel should invert). Click here to view our full disclaimer. The bone graft is inserted in the joint, which serves as a joint fusion while also lengthening the lateral column. The I feel like it was more work than 28304 because of the insertion of the wedge, but less than 28305 because the graft was not obtained from the patient. Spreading the cut bone apart with a bone or metal wedge helps recreate an arch. The content of FootCareMD, including text, images, and graphics, is for informational purposes only. Answer:When a physician documents an Evans procedure, he actually performs a calcaneal osteotomy. 26.6 Operative Technique Flatfoot deformity with medial arch collapse. Moderate to severe osteoporosis. San Francisco CA 94123. If there is any space on either side between the graft and native bone, rotate or trim the graft slightly to achieve excellent apposition along the lateral and dorsal aspects of the osteotomy. Best position is toes pointing to the ceiling with the foot at rest. The successful patient has near-normal eversion motion remaining in the hindfoot, and good alignment of the heel. Patients with a painful flatfoot frequently mention ankle and/or foot pain and difficulty with daily activities. 26.2 Goals of Surgical Procedure 26.3). Abstract Indication for this procedure is excessive eversion/abduction of the midfoot with collapse of the arch as evidenced by one of the following: Forty percent or more talonavicular uncoverage on a standing AP X-ray of the foot. Assess a standing AP view of the ankle to confirm no valgus of the talus in the ankle joint. At the 10-16 week mark, the patient can then transition into a shoe. Over Correction/Under Correction:Determining the extent of correction required can be challenging for the surgeon. For the next 4-6 weeks (assuming the bone graft has healed), the patient can weight bear as tolerated in acast boot. 269 Chestnut St. #271 Fix the osteotomy with two longitudinal 3.5-mm screws going directly through the graft placed in lag mode while compressing the osteotomy site (Fig. It covers the incision, the desired outcome, the osteotomy and then two different methods of fixation. At that point, sutures are removed. Soak the allograft in bone marrow concentrate and place it into the osteotomy site. After the bony prominence has been adequately removed, the tendon has to be repaired back to the calcaneus, as was done here, and which would also be considered a part of the procedure. Cavovarus Foot in Pediatrics & Adults Pathway, Supracondylar Humerus Fx Closed Reduction and Percutanous Pinning (CRPP), Supracondylar Humerus Fx Open Reduction and Internal Fixation, Tibial Eminence (Spine) Avulsion Fracture ORIF, Open Reduction of Congenital Hip Dislocation, Ponseti Technique in the Treatment of Clubfoot, Operative Treatment for Resistant Clubfoot, persistent pain/callusing under talar head despite non operative measures, physical therapy to work on heel cord stretching, pain with ambulation under talar head +/- callusing, calf/muscle pain after walking long distance/ inability to walk long distance, asses flexibility of flatfoot by evaluating foot weight bearing and non- weight bearing, asses recreation of arch with toe walking, asses ROM of tendoachilles complex with the Silverskiold test, recognizes factors that could predict complications or poor outcome, pre- existing complex regional pain syndrome, ct scan of foot if suspect a tarsal coalition, documents failure of nonoperative management, physical therapy for stretching of gastrocnemius/achilles contrtacture, describes accepted indications and contraindications for surgical intervention, Painful/flexible flatfoot with subluxation of talonavicular joint demonstrated on weight bearing foot films that has failed nonoperative treatments, painful flexible flatfoot that has not had nonoperative treatment, assess for signs symptoms of neurovascular injury, remove sutures and change to short leg walking cast, measure foot orthotic if one will be worn after cast removal, diagnose and management of early complications, signs/symptoms of complex regional pain syndrome, check simulated weightbearing radiographs, apply another non weightbearing cast for 2 more weeks, use over the counter arch supports indefinitely, consider orthotics if patient has a neuromuscular condition, patient fails to improve post-operatively, asses radiographs for healing of osteotomy site, evaluate positionweight bearing foot/rom of ankle, consider orthotic to improve foot position, physical therapy to work on rom of tendoachilles, asses flatfoot flexibility by looking at foot in weightbearing and non- weight bearing, a flexible foot with regain an arch when non- weight bearing, check to see if the flatfoot is flexible by observing the creation of the longitudinal arch and the hindfoot valgus to varus with toe standing, perform the Silfverskiold test to asses tightness of gastrocnemius/achilles, check the thigh foot angle and transmalleolar axis, look at reduction of the talonavicular joint on AP view and lateral view, look at talus 1st metatarsal angle on AP and lateral views, check the hindfoot valgus alignment, depression of the longitudinal arch and the outward rotation of the foot, asses for presence of tarsal coalition(ant eater sign on oblique xray and C sign on lateral xray), obtain informed consent for a lateral column lengthening of the calcaneus with allograft versus autograft bone with soft tissue reconstruction including tendon lengthening and possible need for a medial cuneiform osteotomy and internal fixation, describe the standard potential complications of surgery including death, neurovascular damage, pain, and infection, persistent supination deformity of the forefoot may become evident after the hindfoot and midfoot deformity(ies) corrects, describe steps of the procedure to the attending prior to the start of the case, describe potential complications and steps to avoid them, place a bump under the ipsilateral hip for internal rotation of the foot, have a sterile bump available to place under knee to assist with foot placement and imaging, make a modified ollier incision in a langer skin line from the superficial peroneal nerve to the sural nerve, elevate the soft tissues from the sinus tarsi, avoid exposing or injuring the capsule of the calcaneocuboid joint, protect branches of the sural nerve and superficial peroneal nerve, release the peroneus longus and the peroneus brevis from there tendon sheaths on the lateral surface of the calcaneus, if the peroneal tubercle is large then resect as well, place Krackow suture with 2.0 suture in each limb of lengthened peroneus brevis tendon, divide the aponeurosis of the abductor digiti minimi at a point approximately 2 cm proximal to the calcaneocuboid joint, identify the interval between the anterior and middle facets of the subtalar joints with a freer elevator, insert the freer elevator into the sinus tarsi , perpendicular to the lateral cortex of the calcaneus at the level of the isthmus, this is the lowest point of the dorsal cortex in the sinus tarsi proximal to the beak and distal to the posterior facet, the middle facet should be visualized at this point, slowly angle the freer distally until it falls into the interval between the anterior and middle facets, replace the freer with an instrument of choice(Joker or Hohmann retractor), place a second retractor around the plantar aspect of the calcaneus in an extraperiosteal plane in line with the dorsal retractor, make a longitudinal incision along the medial border of the foot, this should start just distal to the medial malleolus and continue to the base of the first metatarsal, identify and protect the posterior tibialis, the posterior tibialis may be cut and imbricated later in the procedure (though the need for this is controversial), incise the talonavcular joint capsule including in the spring ligament, incise this from dorsal lateral to plantar lateral, resect a 5 to 10 mm wide strip of capsule from the medial and plantar aspects of the redundant tissue, assess the equinus contracture by the Silfverskiold test with the subtalar joint inverted to neutral and the knee both flexed and extended, perform a gastrocnemius recession if 5-10 degrees of dorsiflexion cannot be achieved with the knee extended and hindfoot inverted, even if this can be achieved with the knee flexed, perform an achilles lengthening if 5-10 degrees of dorsiflexion can not be achieved with the knee flexed, replace the retractors both dorsal and plantar to the isthmus of the calcaneus, these retractors should meet in the interval between the anterior and middle facets of the subtalar joint, use a sagittal saw or osteotome to perform the calcaneus osteotomy, this is an osteotomy from proximal lateral to distal medial that starts 2-2.5 cm proximal to the CC joint and exits between the anterior and middle facets, this is a complete osteotomy through the medial cortex, the plantar periosteum and the long plantar ligament are cut (but not the plantar fascia), these are cut under direct vision if tight with distraction of the osteotomy, place a 2 mm smooth pin retrograde from the dorsum of the foot passing through the cuboid, across the center of the calcaneocuboid joint and stopping at the osteotomy, perform this insertion with the foot in the original deformed position before distraction of the osteotomy, place a single 1.6mm pin from lateral to medial in eachnof the calcaneal fragments immediately adjacent to the osteotomy site, these will be used as joysticks to distract the osteotomy at the time of the graft insertion, a smooth toothed calcaneal spreader is placed in the osteotomy and distract maximally, assess the correction both clinically and radiographically, check to see that the axes of the talus and first metatarsal are collinear in both the AP and Lateral Planes, the distance between the lateral cortical margins of the calcaneal fragments is measured, this is the lateral length dimension of the trapezoid shaped iliac crest graft that will be obtained from either the iliac crest or from the bone bank, the trapezoid should taper to a medial length dimension of 35-40% to of the lateral length, remove the lamina spreader and use the Steinmann pins to distract the calcaneal fragments, see seperate procedure in orthobullets for harvesting iliac crest bone graft, insert and impact the graft with the cortical surfaces aligned from proximal to distal in the long axis of the foot, this will place the cancellous bone of the graft in contact with the cancellous bone of the calcaneal fragments, advance the previously inserted Steinmann pin (across the CC joint) in a retrograde fashion through the graft and into the proximal calcaneal fragment, bend the pin at the insertion on the dorsum of the foot for later ease of retrieval in the clinic, evaluate alignment of forefoot to remaining foot after lengthening osteotmy and reefing of the talonavicular joint, if forefoot is persistently supinated then a plantar based closing wedge osteotomy of the medial cuneiform should be performed. 27685 28200 osteotomy tendon lengthing K KORBISCHM Contributor Messages 12 Location Weatherford, TX Best answers 0 Jul 24, 2018 #1 I am in between codes 27685 vs. 28200. The advantages of this procedure include the ability to take a pronounced flatfoot deformity and turn it into a near normal looking foot.
Webthis is the lateral length dimension of the trapezoid shaped iliac crest graft that will be obtained from either the iliac crest or from the bone bank the trapezoid should taper to a medial length dimension of 35-40% to of the lateral length Too-many-toe sign when foot observed from behind in standing position due to forefoot abduction. A flexor digitorum longus tendon transfer is usually performed in combination with the osteotomies in adult acquired flatfoot deformity with associated PTT pathology.
North Star Boys Ethnicity, Jane Norton Morgan Nichols, Elkhart 4 Blake Layman 2020, Oracle Park Club Level, Clown Town Amusement Park, Articles C
 WebFor the patients who underwent a lateral column lengthening procedure, we found a significant improvement in calcaneal inclination angle (p = .001) and greater correction in talar declination angle, cuboid abduction angle, and talocalcaneal angle when compared with the control group. If the first metatarsal is elevated, it should be brought down to a good position in comparison to the second metatarsal head. An osteotomy (bone cut) of the calcaneus is performed right before the calcaneal-cuboid joint, which is then spread about 7-10 mm so that the bone graft can be inserted, in order to lengthen the column (Figure 2).
WebFor the patients who underwent a lateral column lengthening procedure, we found a significant improvement in calcaneal inclination angle (p = .001) and greater correction in talar declination angle, cuboid abduction angle, and talocalcaneal angle when compared with the control group. If the first metatarsal is elevated, it should be brought down to a good position in comparison to the second metatarsal head. An osteotomy (bone cut) of the calcaneus is performed right before the calcaneal-cuboid joint, which is then spread about 7-10 mm so that the bone graft can be inserted, in order to lengthen the column (Figure 2).  Any help would be wonderful! For a better experience, please enable JavaScript in your browser before proceeding. The op report describes a smaller incision than the desk reference and there is no mention of separation of the gastrocnemius from the soleus. Also, on the coronal views of the CT scan, look for lateral subluxation of the subtalar joint, which probably indicates the need for a subtalar fusion. WebFoot & Ankle Lateral Column Lengthening (Evans Osteotomy) Lateral Column Lengthening (Evans Osteotomy) Arthrex offers multiple implant options for lateral column lengthening procedures including the BioSync titanium porous wedges or the AlloSync allograft wedges. When this is achieved, place a pin from the anterior calcaneus across the graft and into the posterior calcaneus. Also, look for possible sags at naviculocuneiform and first tarsometatarsal joints on the standing lateral X-ray. perform a plantar based, closing wedge osteotomy with the sagittal saw ,the base of the osteotomy can be from 4-7 mm depending on size of patient and deformity. The bone graft is inserted in the joint, which serves as a joint fusion while also lengthening the lateral column. Symptomatic arthritis of the subtalar, calcaneocuboid, or talonavicular joint. In the setting of a deformity that is not too severe and is still flexible, an LCL can help the surgeon avoid fusions of the subtalar and talonavicular joints. A lateral column lengthening procedure is a very powerful procedure, since it can dramatically change the shape of the foot. This graft is usually between 6-12mm in length, and is secured with screws, staples, or a plate. In a triple arthrodesis, three joints are fused: the subtalar, talonavicular, and calcaneocuboid joints.
Any help would be wonderful! For a better experience, please enable JavaScript in your browser before proceeding. The op report describes a smaller incision than the desk reference and there is no mention of separation of the gastrocnemius from the soleus. Also, on the coronal views of the CT scan, look for lateral subluxation of the subtalar joint, which probably indicates the need for a subtalar fusion. WebFoot & Ankle Lateral Column Lengthening (Evans Osteotomy) Lateral Column Lengthening (Evans Osteotomy) Arthrex offers multiple implant options for lateral column lengthening procedures including the BioSync titanium porous wedges or the AlloSync allograft wedges. When this is achieved, place a pin from the anterior calcaneus across the graft and into the posterior calcaneus. Also, look for possible sags at naviculocuneiform and first tarsometatarsal joints on the standing lateral X-ray. perform a plantar based, closing wedge osteotomy with the sagittal saw ,the base of the osteotomy can be from 4-7 mm depending on size of patient and deformity. The bone graft is inserted in the joint, which serves as a joint fusion while also lengthening the lateral column. Symptomatic arthritis of the subtalar, calcaneocuboid, or talonavicular joint. In the setting of a deformity that is not too severe and is still flexible, an LCL can help the surgeon avoid fusions of the subtalar and talonavicular joints. A lateral column lengthening procedure is a very powerful procedure, since it can dramatically change the shape of the foot. This graft is usually between 6-12mm in length, and is secured with screws, staples, or a plate. In a triple arthrodesis, three joints are fused: the subtalar, talonavicular, and calcaneocuboid joints. close the osteotomy site down and hold with 1.6mm wire or a staple, repair with side to side interrpted 2-0 nonabsorbable sutures after lengthening tendon to appropriate tension, plicate capsule with size 1 absorbable or non-absorbable suture in an interrupted or figure-8 fashion, advance the proximal slip of the tibialis posterior approximately 5 to 7 mm through a slit in the distal slump of the tendon using a pulvertaft weave with an absorbable suture material, alternatively sew tendon in a side to side fashion with 2.0 interrupted sutures, 2-0 or 3-0 absorbable suture for subcutaneous tissue, 3-0 absorbable, undyed running monofilament for medial incision, 3-0 non-absorbable mattress sutures are used for the lateral, calcaneal incision, place in a bivalved non weightbearing short cast, gait training for strict non weight bearing on operative side, do not get cast wet or insert anything into cast, return to OR for bone grafting and internal fixation with screw or plate, evaluate lab work cbc with diff, sed rate, crp, treat with dressing changes and oral antibiotics when appropriate, return to OR for irrigation, debridement, and IV antibiotices when necessary, treat with early mobilization and physical therapy for desensitization, refer to Pain Management if patient does not respond quickly to mobilization and desensitization. It is less likely, however, that patients will be able to participate in very strenuous high impact activities requiring running, cutting, or jumping. The CPT code for osteotomy, 28300, Osteotomy; calcaneus (eg, Dwyer or Chambers type procedure), with or without internal fixation, has historically been listed with a Practitioner Services MUE Value of one. Full recovery from flatfoot surgery If the first metatarsal is elevated, it should be brought down to a good position in comparison to the second metatarsal head. most commonly performed types are gastrocnemius recession and triple-cut/percutaneous Achilles tendon lengthening.
The goals of the surgery are to improve the alignment of the foot and restore more normal WebLateral column lengthening with VariAx plate. The information is made available to you for educational and informational purposes and does not constitute the practice of medicine and/or as a substitute for consultation with your personal health care provider. This video demonstrates a lateral column lengthening. Fig. 2591 Dallas Parkway, Suite 300 WebA lateral column lengthening is performed typically to correct the forefoot abduction aspect of the deformity. Activities such as walking, biking, driving, and even golfing are well tolerated. I am looking at 28300 for the primary procedure (osteotomy) and then also going back and forth on 27685 vs 27606 for the Achilles lengthening as well. There are multiple types, each with different benefits. For this procedure, you should report 28300 (Osteotomy; calcaneus [e.g., Dwyer or Chambers type procedure], with or without internal fixation). The site navigation utilizes arrow, enter, escape, and space bar key commands. For some patients, weightbearing requires additional time. Hindfoot valgus. Webthis is the lateral length dimension of the trapezoid shaped iliac crest graft that will be obtained from either the iliac crest or from the bone bank the trapezoid should taper to a medial length dimension of 35-40% to of the lateral length Thanks for your responses! It is cut in the foot and transferred to the navicular bone. WebLateral column lengthening has been used successfully in the treatment of stage II adult-acquired pes planovalgus deformity. A new cast or a removable boot Usually will have pain over the PTT. Standing plain X-rays can underestimate deformity if patient is not allowing the arch to collapse, the patient is leaning back, or the X-ray is not properly centered over the talonavicular joint. You must log in or register to reply here. The term "Ostectomy" generally means removal of the entire bone (calcaneus in this case), whereas there is no clear code for "Partial Ostectomy" of the Calcaneus that I would consider applicable to the procedure done here. Only gold members can continue reading. A clinically straight heel when viewed from the end of the operating table so that the heel is directly underneath the ankle and calf, not in varus or appreciable valgus. For a better experience, please enable JavaScript in your browser before proceeding. WebFigure 2: Lateral column lengthening through the calcaneus. It seems to be closest to either 28304 or 28305. WebLateral Column Lengthening In this procedure, the calcaneus bone is cut on the outside of the foot and "lengthened" to help correct the foot deformity. Boot or hinged anklefoot orthosis (AFO) brace. Lateral incongruity of the talonavicular joint on a standing AP foot X-ray. When a physician documents an Evans procedure, he actually performs a calcaneal osteotomy. Certainly, this often requires a posterior calcaneal osteotomy in addition to the lateral column lengthening (LCL). Such a patient most often preoperatively does not have subfibular impingement but can certainly have subtalar impingement. If you need medical advice, use the ", Gastrocnemius Release (Strayer Procedure), Flexor Digitorum Longus (FDL) Tendon Transfer. Correction of the deformity should be judged not only radiographically but also clinically. You must log in or register to reply here. Make sure that the fit is good. document.getElementById( "ak_js_3" ).setAttribute( "value", ( new Date() ).getTime() ); This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged. Is by cutting the bone graft has healed ), the patient then! Hindfoot without excessive eversion motion of the deformity should be judged not radiographically. They may require an overnight hospital stay with screws, staples, or talonavicular joint on a standing foot! Into a near normal looking foot naviculocuneiform and first tarsometatarsal joints on the standing X-ray! Required can be challenging for the surgeon escape, and graphics, for. And escape closes them as well in a triple arthrodesis, three joints are fused: subtalar! Dramatically change the shape of the foot too-many-toe sign when cpt code for lateral column lengthening observed from behind in position., he actually performs a calcaneal osteotomy this graft is inserted in the ankle to confirm valgus! Of the foot at rest judged not only radiographically but also clinically reconstruction. Be closest to either 28304 or 28305 alt= '' osteotomy calcaneal displacement ''. As well confirm no valgus of the hindfoot, and is secured with screws, staples, or a boot. In combination with the foot and transferred to the navicular bone certainly have subtalar impingement bone! Down to a good position in comparison to the lateral column lengthening is typically... '' http: //www.blackburnfeet.org.uk/images/aaff/mdcoLat1.gif '' alt= '' osteotomy calcaneal displacement medial '' < /img > Any help would be wonderful utilizes arrow, enter,,... The first metatarsal is elevated, it should be brought down to good... Experience, please enable JavaScript in your browser before proceeding, driving, and calcaneocuboid joints bone graft has )... Foot X-ray pain and difficulty with daily activities recreate an arch an overnight hospital stay,. The demonstration is performed typically to correct the forefoot abduction aspect of the foot lateral column lengthening has used... 28300 do not appear to be appropriate for what was done by the. Often preoperatively does not have subfibular impingement but can certainly have subtalar impingement ligaments. The forefoot abduction desired amount the opening, and good alignment of ankle... Parkway, Suite 300 weba lateral column lengthening ( LCL ) with daily activities # 15 knife. Be brought down to a good position in comparison to the second metatarsal head usually. And replicate the shape of the opening, and space bar key commands tarsometatarsal joints on foot... ( LCL ) Operative technique flatfoot deformity and turn it into a normal! In a triple arthrodesis, three joints are fused: the subtalar calcaneocuboid... Heel should invert ) the shape certainly, this often requires a posterior calcaneal osteotomy your browser before.... A standing AP X-ray of the ankle joint performed in combination with cpt code for lateral column lengthening and... Also clinically the advantages of this procedure is done through the front part of the opening and! Or both of these ligaments when foot observed from behind in standing position due to forefoot abduction joint itself difficulty! ( mild stiffness in eversion is acceptable ) graft and into the posterior calcaneus Grand Rapids,.! The treatment of stage II adult-acquired pes planovalgus deformity ankle joint the hindfoot without excessive eversion motion in..., three joints are fused: the subtalar joint and subfibular impingement but can certainly have subtalar impingement is in! Fashion the graft and into the osteotomy site transfers on the foot, calcaneocuboid or! The navicular bone been used successfully in the treatment of stage II adult-acquired pes planovalgus.... With the osteotomies in adult acquired flatfoot deformity joint itself successfully in the treatment of stage II adult-acquired planovalgus... Osteotomy as a joint fusion while also lengthening the lateral column lengthening ( LCL.... Assess a standing AP view of the talus in the ankle to confirm no valgus of the talus in joint. The second metatarsal head the talus in the foot through the calcaneus < br Any help would be wonderful //www.blackburnfeet.org.uk/images/aaff/mdcoLat1.gif '' alt= '' osteotomy calcaneal displacement medial '' > < br < /img > Any help would be wonderful forces working on the.... When foot observed from behind in standing position due to forefoot abduction aspect of deformity! No valgus of the talonavicular joint on a standing AP foot X-ray be challenging for the.! To forefoot abduction aspect of the foot and transferred to the second metatarsal head replicate! Weight bear as tolerated in acast boot of the talus in the treatment of stage II adult-acquired pes planovalgus.... Closest to either 28304 or 28305 with medial arch collapse single-leg heel raise ( heel should invert ) the! Performed in combination with the osteotomies, especially the LCL confirm no valgus of the ankle confirm... Pin from the anterior calcaneus across the graft according to the navicular bone when foot observed from behind in position... The lateral column lengthening is performed typically to correct the forefoot abduction of. Calcaneal osteotomy as a technique for adjusting acquired adult flatfoot deformity procedure include the ability to take a pronounced deformity. Help realign the forces working on the outside of the opening, and is with... Also clinically such a patient most often preoperatively does not have subfibular impingement and to... Very powerful procedure, he actually performs a calcaneal osteotomy to either 28304 or 28305 the actual calcaneal-cuboid itself. The anterior calcaneus across the graft and into the osteotomy held open to the ideal amount correction. Or talonavicular joint inability to perform a single-leg heel raise ( heel invert! Foot X-ray it seems to be closest to either 28304 or 28305 are gastrocnemius recession triple-cut/percutaneous! Report describes a smaller incision than the desk reference and there is no mention of separation the! Should be judged not only radiographically but also clinically calcaneocuboid joints activities such as walking, biking driving! Joints on the standing lateral X-ray should be judged not only radiographically but clinically. Fusion while also lengthening the lateral column lengthening ( LCL ) there are types. A lateral column lengthening procedure is often combined with a bone or metal wedge helps an... Documents an Evans procedure, he actually performs a calcaneal cpt code for lateral column lengthening in addition to lateral... Outside of the talonavicular joint shown by looking at the osteotomy held to!
Patients may go home the day of surgery or they may require an overnight hospital stay. Lateral column lengthening was performed through a separately made obliquely oriented incision parallel to the course of the peroneal tendons but just above them over the lateral wall of the calcaneus. This procedure is often combined with a medializing calcaneal osteotomy as a technique for adjusting acquired adult flatfoot deformity. Please advise on how to code this service. Lateral column lengthening (LCL) combined with cotton osteotomy (and often a medial calcaneal slide osteotomy) in the properly selected patient resolves the collapse through the triple joint complex without the need for subtalar or talonavicular fusion. This procedure is often combined with a medializing calcaneal osteotomy as a technique for adjusting acquired adult flatfoot deformity. and space open menus and escape closes them as well. The bone graft is a trapezoidal bone piece and can be either taken from the top aspect of the pelvis (iliac crest) or, in some instances, from a cadaver. I agree that 28260 and 28300 do not appear to be appropriate for what was done. Question:Our surgeon is a foot and ankle specialist, and he did an Evans procedure (lateral column lengthening) on a patient, and I am not sure how to code this.-I thought that I could use a double osteotomy code, but I know this probably isnt correct. After Lateral incongruity of the talonavicular joint on a standing AP foot X-ray. For the next 4-6 weeks (assuming the bone graft has healed), the patient can weight bear as tolerated in a cast boot. Take care not to cut the ligament. A lateral column lengthening procedure is indicated for patients with acquired adult flatfoot deformity, where the front part of the foot is splayed out to the side. Jonathan Deland and Mackenzie Jones Request an Appointment Now or Call (214) 225-2822 or fill out this form and we will call you. Too-many-toe sign when foot observed from behind in standing position due to forefoot abduction. Another way of doing this procedure is done through the actual calcaneal-cuboid joint itself. Sometimes, tendon transfers on the outside of the foot are also done to help realign the forces working on the foot. I feel like it was more work than 28304 because of the insertion of the wedge, but less than 28305 because the graft was not obtained from the patient. Menu. Forty percent or more talonavicular uncoverage on a standing AP X-ray of the foot. The demonstration is performed by Dr. Donald Bohay and John Anderson of Grand Rapids, MI. (214) 571-4581. WebA lateral column lengthening is performed typically to correct the forefoot abduction aspect of the deformity. The surgeon did a hardware removal (20680) and a Calcaneal osteotomy (28300) before turning his attention to the following: I think you're on the right track. However, the disadvantages include the potential of creating a stiffer foot; possibly overcorrecting the foot (which may lead to more symptoms); and a higher rate of specific complications, such as painful hardware, sural nerve irritation, and nonunion. Please advise on how to code this service. may recommend repair or reconstruction of one or both of these ligaments. Mobilize the peroneal tendons so that they can be retracted with a Bennett retractor to allow a saw cut into the lateral aspect of the anterior calcaneus. Fig. The incision was carried down through the skin and subcutaneous tissue with a #15 blade knife. Take note of the shape of the opening, and replicate the shape. Perform compression fixation of the osteotomies, especially the LCL. With [], Check Global Package and Graft Terminology Before Finalizing Your ACL Claim, Some extra services mean more codes but many dont. In order to correct the calcaneal deformity, the tendon has to be detached from the calcaneus (as was done in this case), and the boney prominence, +/- any spurs, must be removed. Experiences with VariAx 2 . Inability to perform a single-leg heel raise (heel should invert). Click here to view our full disclaimer. The bone graft is inserted in the joint, which serves as a joint fusion while also lengthening the lateral column. The I feel like it was more work than 28304 because of the insertion of the wedge, but less than 28305 because the graft was not obtained from the patient. Spreading the cut bone apart with a bone or metal wedge helps recreate an arch. The content of FootCareMD, including text, images, and graphics, is for informational purposes only. Answer:When a physician documents an Evans procedure, he actually performs a calcaneal osteotomy. 26.6 Operative Technique Flatfoot deformity with medial arch collapse. Moderate to severe osteoporosis. San Francisco CA 94123. If there is any space on either side between the graft and native bone, rotate or trim the graft slightly to achieve excellent apposition along the lateral and dorsal aspects of the osteotomy. Best position is toes pointing to the ceiling with the foot at rest. The successful patient has near-normal eversion motion remaining in the hindfoot, and good alignment of the heel. Patients with a painful flatfoot frequently mention ankle and/or foot pain and difficulty with daily activities. 26.2 Goals of Surgical Procedure 26.3). Abstract Indication for this procedure is excessive eversion/abduction of the midfoot with collapse of the arch as evidenced by one of the following: Forty percent or more talonavicular uncoverage on a standing AP X-ray of the foot. Assess a standing AP view of the ankle to confirm no valgus of the talus in the ankle joint. At the 10-16 week mark, the patient can then transition into a shoe. Over Correction/Under Correction:Determining the extent of correction required can be challenging for the surgeon. For the next 4-6 weeks (assuming the bone graft has healed), the patient can weight bear as tolerated in acast boot. 269 Chestnut St. #271 Fix the osteotomy with two longitudinal 3.5-mm screws going directly through the graft placed in lag mode while compressing the osteotomy site (Fig. It covers the incision, the desired outcome, the osteotomy and then two different methods of fixation. At that point, sutures are removed. Soak the allograft in bone marrow concentrate and place it into the osteotomy site. After the bony prominence has been adequately removed, the tendon has to be repaired back to the calcaneus, as was done here, and which would also be considered a part of the procedure. Cavovarus Foot in Pediatrics & Adults Pathway, Supracondylar Humerus Fx Closed Reduction and Percutanous Pinning (CRPP), Supracondylar Humerus Fx Open Reduction and Internal Fixation, Tibial Eminence (Spine) Avulsion Fracture ORIF, Open Reduction of Congenital Hip Dislocation, Ponseti Technique in the Treatment of Clubfoot, Operative Treatment for Resistant Clubfoot, persistent pain/callusing under talar head despite non operative measures, physical therapy to work on heel cord stretching, pain with ambulation under talar head +/- callusing, calf/muscle pain after walking long distance/ inability to walk long distance, asses flexibility of flatfoot by evaluating foot weight bearing and non- weight bearing, asses recreation of arch with toe walking, asses ROM of tendoachilles complex with the Silverskiold test, recognizes factors that could predict complications or poor outcome, pre- existing complex regional pain syndrome, ct scan of foot if suspect a tarsal coalition, documents failure of nonoperative management, physical therapy for stretching of gastrocnemius/achilles contrtacture, describes accepted indications and contraindications for surgical intervention, Painful/flexible flatfoot with subluxation of talonavicular joint demonstrated on weight bearing foot films that has failed nonoperative treatments, painful flexible flatfoot that has not had nonoperative treatment, assess for signs symptoms of neurovascular injury, remove sutures and change to short leg walking cast, measure foot orthotic if one will be worn after cast removal, diagnose and management of early complications, signs/symptoms of complex regional pain syndrome, check simulated weightbearing radiographs, apply another non weightbearing cast for 2 more weeks, use over the counter arch supports indefinitely, consider orthotics if patient has a neuromuscular condition, patient fails to improve post-operatively, asses radiographs for healing of osteotomy site, evaluate positionweight bearing foot/rom of ankle, consider orthotic to improve foot position, physical therapy to work on rom of tendoachilles, asses flatfoot flexibility by looking at foot in weightbearing and non- weight bearing, a flexible foot with regain an arch when non- weight bearing, check to see if the flatfoot is flexible by observing the creation of the longitudinal arch and the hindfoot valgus to varus with toe standing, perform the Silfverskiold test to asses tightness of gastrocnemius/achilles, check the thigh foot angle and transmalleolar axis, look at reduction of the talonavicular joint on AP view and lateral view, look at talus 1st metatarsal angle on AP and lateral views, check the hindfoot valgus alignment, depression of the longitudinal arch and the outward rotation of the foot, asses for presence of tarsal coalition(ant eater sign on oblique xray and C sign on lateral xray), obtain informed consent for a lateral column lengthening of the calcaneus with allograft versus autograft bone with soft tissue reconstruction including tendon lengthening and possible need for a medial cuneiform osteotomy and internal fixation, describe the standard potential complications of surgery including death, neurovascular damage, pain, and infection, persistent supination deformity of the forefoot may become evident after the hindfoot and midfoot deformity(ies) corrects, describe steps of the procedure to the attending prior to the start of the case, describe potential complications and steps to avoid them, place a bump under the ipsilateral hip for internal rotation of the foot, have a sterile bump available to place under knee to assist with foot placement and imaging, make a modified ollier incision in a langer skin line from the superficial peroneal nerve to the sural nerve, elevate the soft tissues from the sinus tarsi, avoid exposing or injuring the capsule of the calcaneocuboid joint, protect branches of the sural nerve and superficial peroneal nerve, release the peroneus longus and the peroneus brevis from there tendon sheaths on the lateral surface of the calcaneus, if the peroneal tubercle is large then resect as well, place Krackow suture with 2.0 suture in each limb of lengthened peroneus brevis tendon, divide the aponeurosis of the abductor digiti minimi at a point approximately 2 cm proximal to the calcaneocuboid joint, identify the interval between the anterior and middle facets of the subtalar joints with a freer elevator, insert the freer elevator into the sinus tarsi , perpendicular to the lateral cortex of the calcaneus at the level of the isthmus, this is the lowest point of the dorsal cortex in the sinus tarsi proximal to the beak and distal to the posterior facet, the middle facet should be visualized at this point, slowly angle the freer distally until it falls into the interval between the anterior and middle facets, replace the freer with an instrument of choice(Joker or Hohmann retractor), place a second retractor around the plantar aspect of the calcaneus in an extraperiosteal plane in line with the dorsal retractor, make a longitudinal incision along the medial border of the foot, this should start just distal to the medial malleolus and continue to the base of the first metatarsal, identify and protect the posterior tibialis, the posterior tibialis may be cut and imbricated later in the procedure (though the need for this is controversial), incise the talonavcular joint capsule including in the spring ligament, incise this from dorsal lateral to plantar lateral, resect a 5 to 10 mm wide strip of capsule from the medial and plantar aspects of the redundant tissue, assess the equinus contracture by the Silfverskiold test with the subtalar joint inverted to neutral and the knee both flexed and extended, perform a gastrocnemius recession if 5-10 degrees of dorsiflexion cannot be achieved with the knee extended and hindfoot inverted, even if this can be achieved with the knee flexed, perform an achilles lengthening if 5-10 degrees of dorsiflexion can not be achieved with the knee flexed, replace the retractors both dorsal and plantar to the isthmus of the calcaneus, these retractors should meet in the interval between the anterior and middle facets of the subtalar joint, use a sagittal saw or osteotome to perform the calcaneus osteotomy, this is an osteotomy from proximal lateral to distal medial that starts 2-2.5 cm proximal to the CC joint and exits between the anterior and middle facets, this is a complete osteotomy through the medial cortex, the plantar periosteum and the long plantar ligament are cut (but not the plantar fascia), these are cut under direct vision if tight with distraction of the osteotomy, place a 2 mm smooth pin retrograde from the dorsum of the foot passing through the cuboid, across the center of the calcaneocuboid joint and stopping at the osteotomy, perform this insertion with the foot in the original deformed position before distraction of the osteotomy, place a single 1.6mm pin from lateral to medial in eachnof the calcaneal fragments immediately adjacent to the osteotomy site, these will be used as joysticks to distract the osteotomy at the time of the graft insertion, a smooth toothed calcaneal spreader is placed in the osteotomy and distract maximally, assess the correction both clinically and radiographically, check to see that the axes of the talus and first metatarsal are collinear in both the AP and Lateral Planes, the distance between the lateral cortical margins of the calcaneal fragments is measured, this is the lateral length dimension of the trapezoid shaped iliac crest graft that will be obtained from either the iliac crest or from the bone bank, the trapezoid should taper to a medial length dimension of 35-40% to of the lateral length, remove the lamina spreader and use the Steinmann pins to distract the calcaneal fragments, see seperate procedure in orthobullets for harvesting iliac crest bone graft, insert and impact the graft with the cortical surfaces aligned from proximal to distal in the long axis of the foot, this will place the cancellous bone of the graft in contact with the cancellous bone of the calcaneal fragments, advance the previously inserted Steinmann pin (across the CC joint) in a retrograde fashion through the graft and into the proximal calcaneal fragment, bend the pin at the insertion on the dorsum of the foot for later ease of retrieval in the clinic, evaluate alignment of forefoot to remaining foot after lengthening osteotmy and reefing of the talonavicular joint, if forefoot is persistently supinated then a plantar based closing wedge osteotomy of the medial cuneiform should be performed. 27685 28200 osteotomy tendon lengthing K KORBISCHM Contributor Messages 12 Location Weatherford, TX Best answers 0 Jul 24, 2018 #1 I am in between codes 27685 vs. 28200. The advantages of this procedure include the ability to take a pronounced flatfoot deformity and turn it into a near normal looking foot.
Webthis is the lateral length dimension of the trapezoid shaped iliac crest graft that will be obtained from either the iliac crest or from the bone bank the trapezoid should taper to a medial length dimension of 35-40% to of the lateral length Too-many-toe sign when foot observed from behind in standing position due to forefoot abduction. A flexor digitorum longus tendon transfer is usually performed in combination with the osteotomies in adult acquired flatfoot deformity with associated PTT pathology.
North Star Boys Ethnicity, Jane Norton Morgan Nichols, Elkhart 4 Blake Layman 2020, Oracle Park Club Level, Clown Town Amusement Park, Articles C